WHY BUCKWHEAT IS AN IMPORTANT STAPLE CROP IN NEPAL ?

Buckwheat (Fagopyrum spp.) Is generally known as 100 days crop and is one of the major food crops in the high hill region of Nepal. It is an important crop in terms of its adaptation to diverse climatic conditions, moisture stress regime, nutrients limitation and cool Temperature and it fits to different patterns of cropping systems because of its short growing period. Buckwheat plants are able to do well on marginal land with or without fertilizer supplements. It has widespread uses and it is also an environmentally friendly crop. Therefore it is a useful staple crop of Nepal.
Buckwheat posses high nutritional and medicinal value and it is used as raw materials for production of different food items and also used as fuel, fodder, feed and bedding material for live stock . And it also posses cultural value in mountain and hilly region of Nepal. It contains high percentage of essential amino acids like lysine and tryptophan as compared to other cereal crops. Beside it is a good source for high quality amino acid of 18-20 type having biological. Buckwheat is an natural functional food and regarded highly not only for its balanced amino acid makeup, high value of protein and favourable fat composition but primarily for its high rutin content. Rutin is an important therapeutic substance that favourably influence the increase of blood vessels, elasticity, the treatment of circulating disorders and a theroscelosis, the reduction of blood pressure and stimulates the organism to utilize the vitamin C. Buckwheat can show positive effects on human health such as antioxidant, antihypertensive, antidiabetic, neuroprotective and hypocholesterolemic effects due to its rich and diverse nutritional content.
NUTRIENT COMPOSITION OF COMMON BUCKWHEAT
Dry matters:
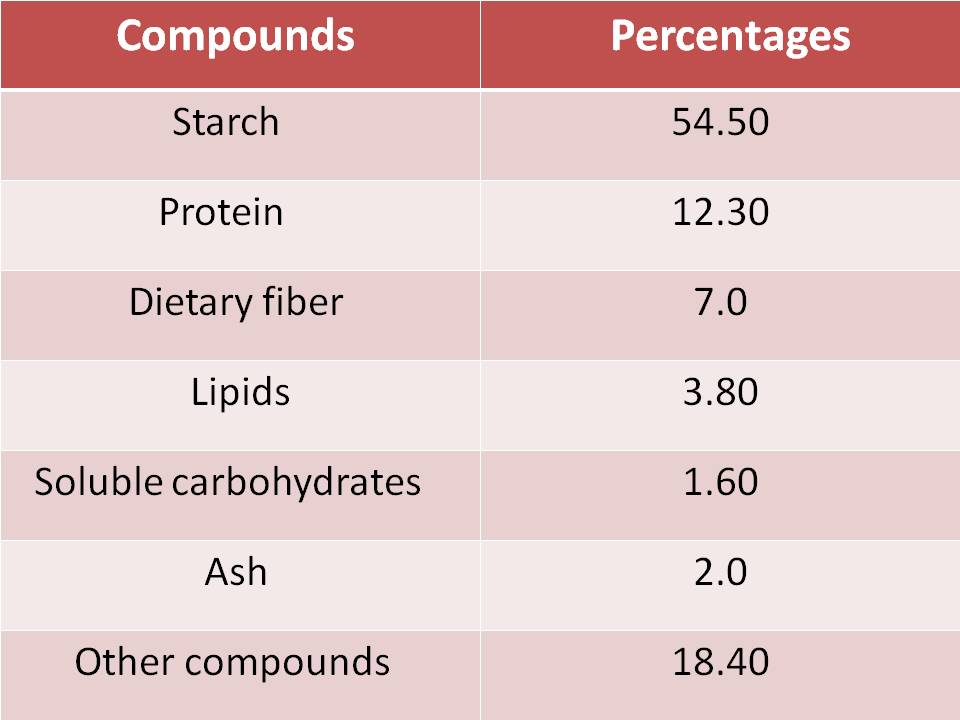
Fresh weight:
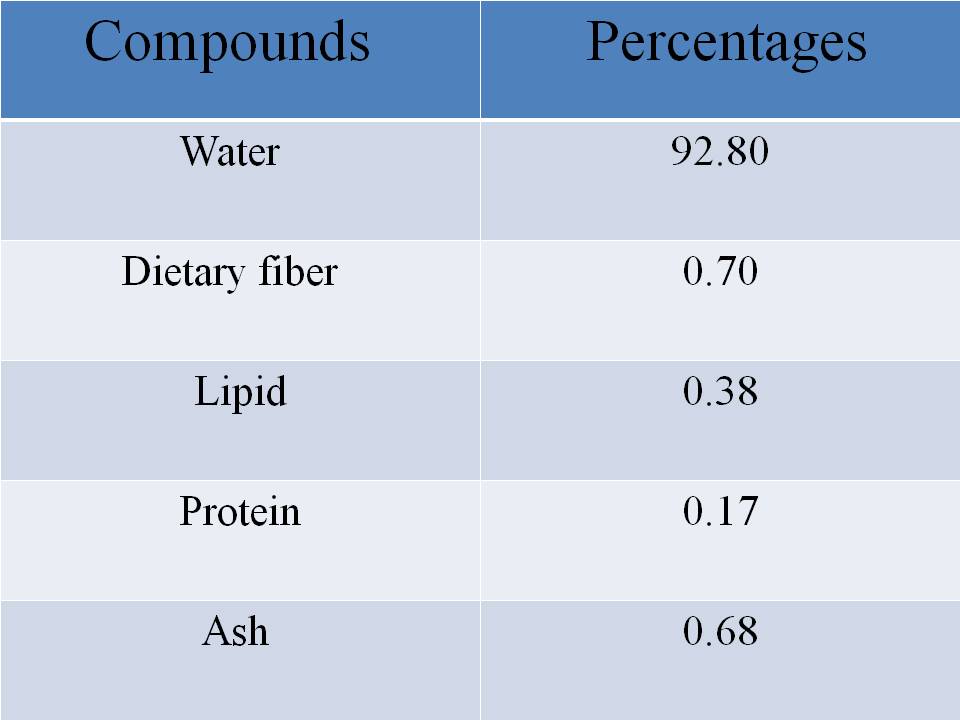
IMPORTANCE AND USES OF BUCKWHEAT
Buckwheat as food:
- Both tite and mithe buckwheat are used to make bread.
- The flour of tite type of buckwheat is used to make dhido while whole and crushed grain of both types of buckwheat are cooked as rice.
- When flour of buckwheat is mixed with flour of other grains, tite type gives yellowish colour while mithe gives grayish colour.
- Buckwheat grains are used to prepare local alcohol.
- The Morden recipes of buckwheat are not yet introduced to rural farmer.
- Tender plant leaves are used for fresh vegetables and also used as tea and green salad.
- Dried leaves are also used as vegetables during off season after boiling.
- Tender and plant leaves are used to make pickles.
Medicinal importance :
- Thick bread of buckwheat is eaten when it is hot for gastric problems.
- People use tite buckwheat as a food for stomach problems.
- Buckwheat flour paste is used for tonsil problems.
- For cold, cough, and fever paste of tite buckwheat is applied in the throat, forehead and nose.
- Buckwheat is used to check pneumonia in children.
- For gum bleeding and swelling flour of tite buckwheat is applied.
- Fresh flour of tite buckwheat is used for allergies like skin drying and itching.
- Soup of buckwheat in boiled water is used for jaundice patients.
- Buckwheat is used to reduce the effect of poison in body.
Religious and cultural importances:
- In some parts of himalayan tite, buckwheat bread is offered to God in the full moon of Kartik.
- In the full moon of magh, a ball prepared of tite buckwheat is offered to the God.
- Tite buckwheat grains are also popped to worship in chaite puja.
- Buckwheat is scared cereal and farmers believe that God like.
Buckwheat for livestock:
- Buckwheat flour is given mostly to the animal at the time of parturition and gestation period.
- Buckwheat flour is good food for young calves.
- Buckwheat is also used as fodder, feed and bedding material for livestock.

